- Farm & Garden
- Pumps & Motors
- Food Processing
- Workshop, DIY & MRO
- Lab & Measuring Tools

Brand: Imperium
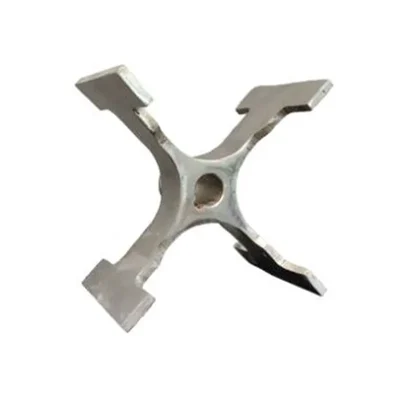
Impeller For Pulverizer Of 5 HP (Brand- Imperium)
SKU: TI-IF-39960 Estimated Delivery By: Mar 9 - Mar 11
Estimated Delivery By: Mar 9 - Mar 11 




MRP : ₹8000 ₹7565
5% OFF!
 Estimated Delivery By: Mar 9 - Mar 11
Estimated Delivery By: Mar 9 - Mar 11 

Easy Return
& Refund
& Refund

Quality
Assurance
Assurance

Trusted
Delivery
Delivery

After Sales
Assistance
Assistance

Buyer
Protection
Protection
₹7565 (Including GST)
MRP : ₹8000
5% OFF!
Get Extra ₹113 OFF on Prepaid Orders
QTY :
-
1
+
Short Description
Impeller For Pulverizer
Quantity 1 piece
Country of origin: India
Specifications
- Brand: Imperium
- Weight (Approx.) : 12 kg
- Quantity : 1
- Material - Stainless steel
* Note: Suitable Only For Imperium Brand
Description
This Impeller For Pulverizer machine is a critical rotating component responsible for the grinding and crushing action within the machine. Driven by the 5 horsepower motor, this robust part typically consists of a central hub with multiple beaters, hammers, or blades (depending on the pulverizer's design) attached to it. As it spins at high speeds, the impeller creates impact and shear forces that break down various materials into a finer particle size, making it indispensable for processes requiring efficient pulverization.
Features
:Optimized for 5 HP Motor: Specifically designed and balanced to work efficiently with a 5 horsepower motor, ensuring optimal performance and power transfer.
- Durable Construction: Typically manufactured from high-grade, wear-resistant materials such as hardened steel, mild steel (MS), or alloy steel, to withstand abrasive materials and high impact forces
- High-Speed Rotation: Engineered to operate at high RPMs, generating the necessary kinetic energy for effective material pulverization.
- Balanced Design: Precision-machined and balanced to minimize vibration and extend the lifespan of both the impeller and the pulverizer itself.
- Configurable Blades/Hammers: May feature fixed blades, swing hammers, or a combination, depending on the type of material being processed and the desired output fineness.
- Easy Installation/Replacement: Designed for relatively straightforward installation and replacement, facilitating maintenance and reducing downtime.
- Corrosion Resistance (Optional): Some impellers may be treated or made from materials with enhanced corrosion resistance for processing certain chemicals or moist materials.
Applications
:Grain and Cereal Grinding: Used extensively in agricultural and food processing industries for pulverizing grains like corn, wheat, rice, and spices into flour or feed.
Herb and Spice Processing: Crucial for grinding dried herbs, spices (e.g., chili, turmeric, cumin), and medicinal plants into fine powders for culinary, pharmaceutical, or cosmetic uses.
Chemical and Mineral Processing: Employed in industries to crush and reduce the particle size of various chemicals, minerals, pigments, and other non-abrasive materials.
Waste and Biomass Reduction: Can be utilized for breaking down certain types of dry waste, agricultural residues, or biomass materials for composting, energy production, or further processing.
Usage
:Installation: Ensure the pulverizer's power is disconnected. Carefully mount the impeller onto the motor shaft, aligning it correctly and securing it tightly with appropriate fasteners (e.g., nuts, bolts, keys) according to the pulverizer's manual.
Pre-Operation Check: Before starting, verify that the impeller is securely fastened, rotates freely without obstruction, and that all safety guards are in place. Check for any signs of wear or damage to the impeller.
Material Feeding: Gradually feed the material to be pulverized into the pulverizer's hopper. Avoid overloading the machine, as this can strain the motor and impeller, leading to inefficiency or damage. The 5 HP motor ensures a good feed rate for its capacity.
Monitoring Operation: During pulverization, listen for unusual noises or vibrations, which could indicate an issue with the impeller or material feeding. Ensure the 5 HP motor is running smoothly and not overheating.
Post-Operation Maintenance: After use, disconnect power. Inspect the impeller for any material buildup, wear, or damage. Clean the impeller and pulverizer chamber to prevent cross-contamination and ensure optimal performance for future use. Regular inspection and replacement of worn parts are crucial for longevity.

Select attribute