- Farm & Garden
- Pumps & Motors
- Food Processing
- Workshop, DIY & MRO
- Lab & Measuring Tools
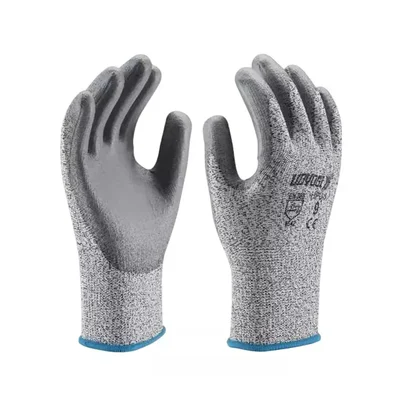

Brand: Udyogi
Udyogi PE Cut Resistant Gloves Grey Color, 9 Size, HPU3 (Pack-1 Pair)
SKU: TI-UP-29644-C1-R64 Delivery By: Feb 10 - Feb 12
Delivery By: Feb 10 - Feb 12 




MRP : ₹400 ₹186
54% OFF!
 Delivery By: Feb 10 - Feb 12
Delivery By: Feb 10 - Feb 12 
Easy Return
& Refund
& Refund

Quality
Assurance
Assurance

Trusted
Delivery
Delivery

After Sales
Assistance
Assistance

Buyer
Protection
Protection
₹NaN (Including GST)
MRP :
Get Extra ₹ OFF on Prepaid Orders
QTY :
Short Description
Specifications
Description

Select attribute