- Farm & Garden
- Pumps & Motors
- Food Processing
- Workshop, DIY & MRO
- Lab & Measuring Tools

Brand: Gravitech
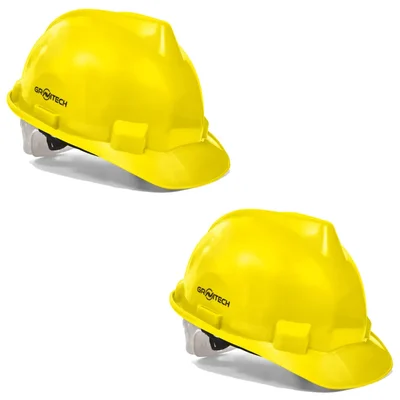
Gravitech Pack of 2, 6, 20 Yellow HDPE Safety Helmet Pin Lock Type Adjustment for Industrial Use (STRONG CAP-P)(Pack-2 pcs)
SKU: TI-SS-30137-C1-R43 Delivery By: Feb 26 - Feb 28
Delivery By: Feb 26 - Feb 28 




MRP : ₹600 ₹383
36% OFF!
 Delivery By: Feb 26 - Feb 28
Delivery By: Feb 26 - Feb 28 
Easy Return
& Refund
& Refund

Quality
Assurance
Assurance

Trusted
Delivery
Delivery

After Sales
Assistance
Assistance

Buyer
Protection
Protection
₹NaN (Including GST)
MRP :
Get Extra ₹ OFF on Prepaid Orders
QTY :
Short Description
Specifications
Description

Select attribute