- Farm & Garden
- Pumps & Motors
- Food Processing
- Workshop, DIY & MRO
- Lab & Measuring Tools

Brand: Generic ( Made in India )
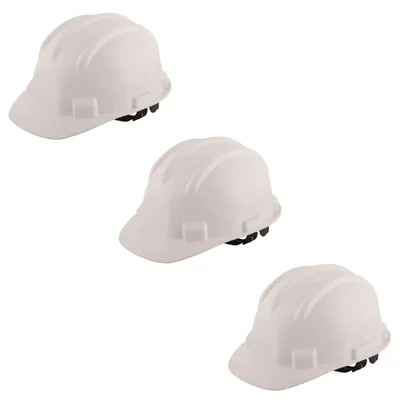
Heavy Duty Pack of 3 Ratchet Safety Helmet, White Colour, Hard Hat For Construction and Industrial Work
SKU: TI-SS-30580 Delivery By: Feb 10 - Feb 12
Delivery By: Feb 10 - Feb 12 




MRP : ₹820 ₹582
29% OFF!
 Delivery By: Feb 10 - Feb 12
Delivery By: Feb 10 - Feb 12 
Easy Return
& Refund
& Refund

Quality
Assurance
Assurance

Trusted
Delivery
Delivery

After Sales
Assistance
Assistance

Buyer
Protection
Protection
₹582 (Including GST)
MRP : ₹820
29% OFF!
Get Extra ₹9 OFF on Prepaid Orders
QTY :
-
1
+
Short Description
Heavy Duty Industrial Safety Helmet With Hard Hat
Material Plastic
Free Size
Country of origin: India
Specifications
- Brand: Generic ( Made in India )
- Weight (Approx.) : 600 gm
- Ideal For : Men and Women
- Helmet Type : Ratchet
- Net Quantity : 3 pcs
- Material: Plastic
- Size: Free Size
- Chin Strap: Nylon
- Ideal For: Men, Women
- Colour: White
Description
A safety helmet is a crucial piece of personal protective equipment (PPE) designed to safeguard the head from injuries in various workplaces. Safety helmets play a vital role in protecting workers’ heads from potential workplace hazards and ensuring their safety while on duty.
Features
:- Impact Resistance: Safety helmets are constructed with tough outer shells which provide excellent impact resistance to protect against falling objects and other hazards.
- Ventilation: Many safety helmets feature ventilated designs that enhance airflow, making them suitable for hot and humid conditions. This helps keep the wearer comfortable during extended use.
- Flame Resistance: Many helmets are designed to be flame-resistant, providing additional protection in environments where exposure to fire is a risk.
Applications
:- Construction: Crucial for shielding employees from falling equipment and supplies on building sites.
- Mining: Offers protection for the head in areas with falling boulders and large machinery.
- Manufacturing: Employed in industries where overhead hazards or machinery pose a risk of head injuries.
- Roadworks: Guards against possible effects for employees engaged in road construction and upkeep.
- Heavy engineering and aviation: Fit for settings with potentially dangerous and large machinery.

Select attribute